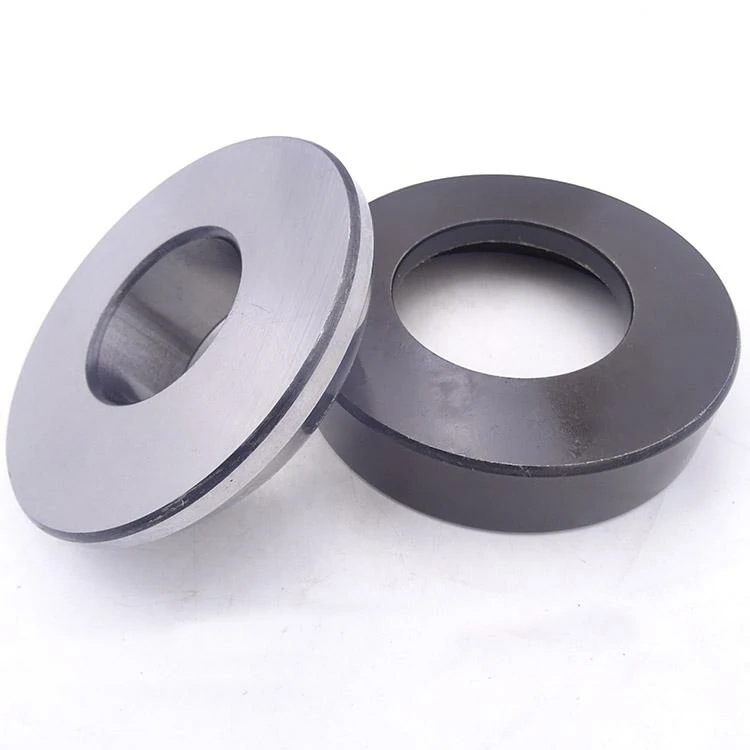
Напречни сферични плъзгащи лагери
Application of Thrust spherical plain bearings:
Engineering machinery: widely used in equipment such as hydraulic cylinder end supports and push mechanisms that need to withstand large axial forces.
Power equipment: used for switches, isolators and other mechanisms, especially suitable for working in high temperature and low maintenance environments.
Metallurgical equipment: such as continuous casting machine supports, rolling mill equipment, etc., need to withstand periodic impact loads and high temperature environments.
Rail transportation: railway supports, steering systems, etc., have small space requirements and high load-bearing capacity, suitable for self-lubrication and low maintenance occasions.
Agricultural and forestry machinery: In articulated parts, pressure push rods and other parts, it has strong anti-fouling ability and is suitable for outdoor dust environments.
Features:
High load-bearing capacity; self-lubricating characteristics, reducing maintenance requirements; compact structure; strong anti-pollution
Strong high temperature resistance; good quietness and vibration suppression.
Thrust spherical plain bearings overview
Натиск Сферични плъзгащи лагери are a type of sliding bearing designed for axial loads, combining the force structure of traditional thrust ball bearings with the friction characteristics of sliding bearings. Its operation depends on the sliding action between spherical contact and low-friction materials, rather than rolling elements.
Main function: suitable for single axial force conditions, not recommended for radial loads.
Basic structure: usually composed of a fixed ring, a rotating ring, and a spherical sliding gasket. The sliding material is mostly PTFE, copper-based alloy or composite lubricating material.
Common materials: a metal support layer (such as carbon steel, copper) combined with a non-metallic composite layer with self-lubricating properties is used to achieve long-term stable operation.

Parameter table of common models
Общоприети марки
SKF Thrust spherical plain bearings
NSK Thrust spherical plain bearings
NTN Thrust spherical plain bearings
KOYO Thrust spherical plain bearings
FAG Thrust spherical plain bearings
INA Thrust spherical plain bearings
TIMKEN Thrust spherical plain bearings
NACHI Thrust spherical plain bearings
Typical application scenarios and functional value
Application field Typical component examples Application value description
Engineering equipment Push device, hydraulic cylinder connection part Effectively alleviate axial impact, with high wear resistance
Electrical system High-voltage disconnector and other mechanisms Can work stably under high temperature and low maintenance conditions
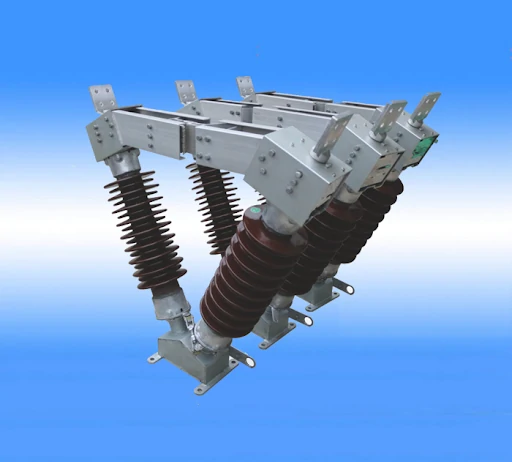
Metallurgical equipment Rolling mill device, continuous casting slider support point Can withstand repeated impact loads and adapt to high temperature working environment

Urban rail transit Bogie articulation system, support connection point Compact structure, strong load-bearing capacity, no lubrication and low maintenance requirements
Agricultural and forestry machinery Thrust rod ends, rotary hinge parts have outstanding dust and pollution resistance, suitable for harsh outdoor environments
Key performance and significant advantages
Performance characteristics Application advantage description
High axial load capacity Can absorb large impact loads, especially suitable for heavy load operation
Self-lubricating operation No need to add lubricating grease, reduce maintenance costs, and improve equipment reliability
Compact structure design Save equipment space, suitable for limited structural layout and compact connection parts
Excellent pollution resistance Materials and structures can effectively block dust and water vapor, adapt to harsh working conditions
Good heat resistance Specific materials can withstand temperatures of 200℃ and above, suitable for high-temperature industrial equipment
Quiet and low-vibration operation Sliding contact mode brings a smoother operating experience, suitable for occasions with strict vibration requirements
Често задавани въпроси (ЧЗВ)
Q1: How is it different from thrust rolling bearings?
A1: Rolling bearings rely on balls or rollers to transfer loads and are suitable for high-speed conditions; while sliding bearings are more suitable for slow speeds, frequent impacts or inconvenient maintenance, and have stronger wear resistance and self-lubricating properties.
Q2: Is this type of bearing completely lubrication-free?
A2: Most models use PTFE or composite materials, which have long-term self-lubricating function; grease can be used to enhance life and stability under extreme conditions.
Q3: How to improve its service life?
A3:
Select models that match the working conditions reasonably;
Avoid loads in non-design directions;
Use corresponding materials in high temperature or corrosive environments;
Regularly check the wear of mounting surfaces and mating parts.
Q4: Can it be used to replace traditional thrust ball bearings?
A4: In low speed, high load, intermittent or pulsed motion, and occasions where frequent lubrication is not possible, it is an ideal alternative to traditional thrust ball bearings and provides a longer maintenance-free cycle.
Conclusion and Summary
Classification Key Points
📌 Definition Thrust spherical plain bearings carry axial loads through spherical contact sliding, and have the characteristics of self-lubrication and simple structure.
🏭 Application Field Widely used in heavy-load axial support points such as industrial machinery, urban transportation, power equipment, and metallurgical equipment.
⭐ Comprehensive advantages Strong load-bearing, self-lubricating, wear-resistant, corrosion-resistant, compact structure, and stable operation.
❓ User focus Superior performance in terms of substitutability, service life, self-lubricating properties, and adaptability to harsh environments.



