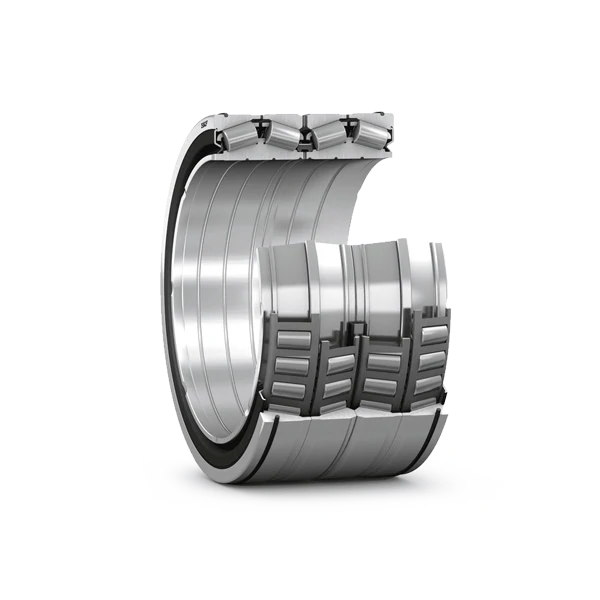
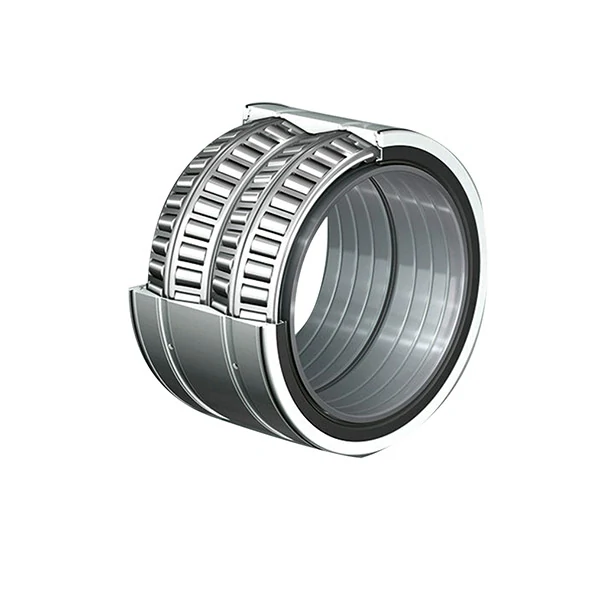
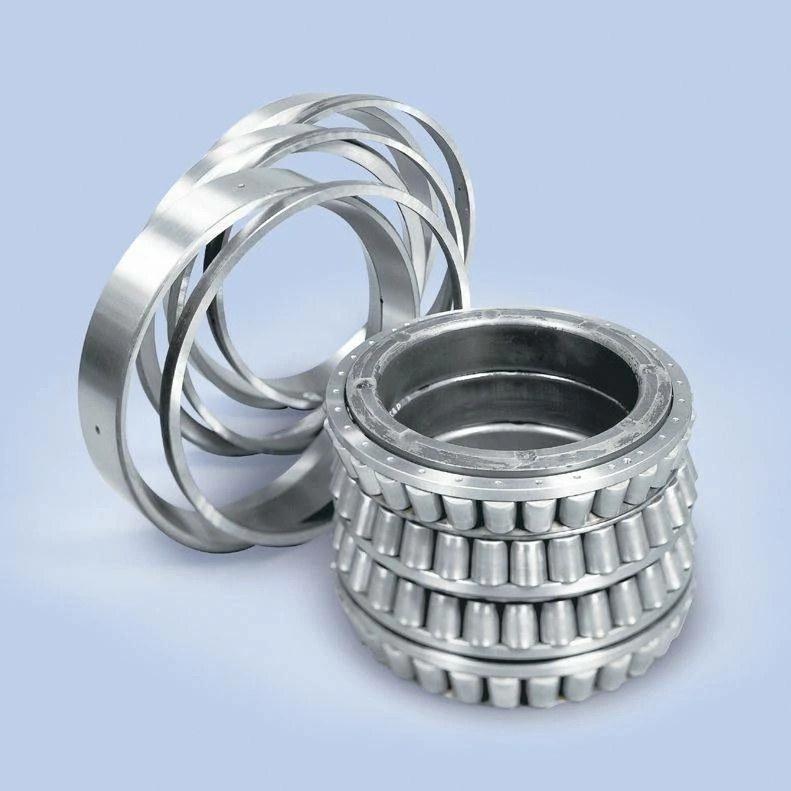
Roulements à rouleaux coniques à quatre rangées
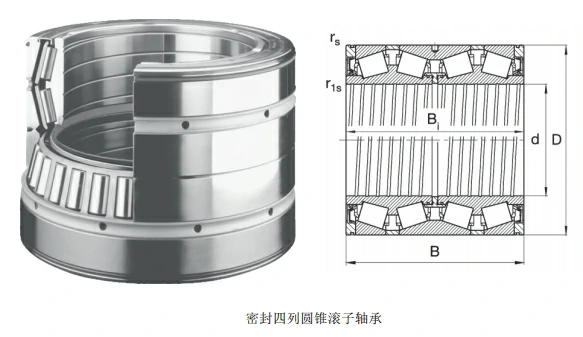
Four-row tapered roller bearings adopt the design of tapered rollers and inner and outer ring contact angles, which can bear radial and axial composite loads at the same time. Compared with single-row or double-row bearings, its four-row roller structure greatly improves the load-bearing capacity and is suitable for industrial scenarios with high load, high speed and high precision requirements.
Overview of Four-row Tapered Roller Bearings
Four-row tapered roller bearings adopt the design of tapered rollers and inner and outer ring contact angles, which can bear radial and axial composite loads at the same time. Compared with single-row or double-row bearings, its four-row roller structure greatly improves the load-bearing capacity and is suitable for industrial scenarios with high load, high speed and high precision requirements.\
Core Features
Ultra-high load-bearing performance
Four rows of rollers evenly distribute the load, significantly improve the radial and axial load limits of the bearing, and are suitable for extreme working conditions.
Excellent wear resistance
The optimized tapered roller contact angle design reduces local stress, reduces wear and prolongs service life.
Wide applicability
It has both radial and axial load capacity and adapts to complex force environments, such as impact loads or alternating stresses.
Reliable sealing protection
Standard sealing or dustproof structure effectively blocks pollutants and ensures stable operation of bearings in harsh environments such as dust and moisture.
Typical model parameter comparison
Parameter description
Dynamic/static load: reflects the maximum load-bearing capacity of the bearing in the rotating and stationary states respectively.
Size and weight: directly affect the equipment structure design and installation space.
Common brands
SKF Four-row tapered roller bearings
NSK Four-row tapered roller bearings
NTN Four-row tapered roller bearings
FAG Four-row tapered roller bearings
INA Four-row tapered roller bearings
KOYO Four-row tapered roller bearings
TIMKEN Four-row tapered roller bearings
NACHI Four-row tapered roller bearings
Typical application areas
Automobile manufacturing: key components such as drive axles and hub units to cope with high-speed rotation and composite stress.
Rail transportation: locomotive axles and gearboxes to meet high load and long-term durability requirements.
Metallurgical industry: rolling mill roller system, continuous casting equipment, withstand high temperature, heavy load and impact conditions.
Energy equipment: wind turbine main shaft, hydraulic turbine, adapt to variable load and harsh environment.
Precision machine tools: spindle support system to ensure high-precision processing and low-vibration operation.
Common problem analysis
Q1: Applicable temperature range?
Conventional models can work in an environment of -20℃ to 120℃, and special lubrication or materials can be extended to higher temperatures.
Q2: How to maintain effectively?
Monitor the lubrication status regularly and replace the grease in time.
Clean the surrounding environment of the bearing to prevent impurities from intruding.
Check for abnormal noise, temperature rise or vibration, and troubleshoot faults in advance.
Q3: How to determine the load capacity?
It is necessary to comprehensively consider the dynamic load (Cr), static load (Cor) and actual working conditions (speed, force direction) for selection and calculation.
Q4: Does it support high-speed operation?
It is suitable for high-speed scenarios, but it needs to be combined with high-performance lubricants and control temperature rise to avoid performance degradation.
Conclusion
Four-row tapered roller bearings are an ideal choice for heavy-load, high-speed and precision equipment due to their high rigidity, long life and adaptability to multiple working conditions. Through scientific selection and standardized maintenance, the operating efficiency of the equipment can be maximized, covering the core needs of key industries such as automobiles, energy, and metallurgy.



